Projects
We list below the SCIENTIFIC PROJECTS active in YEAR 2026 in which the Research and Innovation Center is involved as a coordinator or scientific partner.
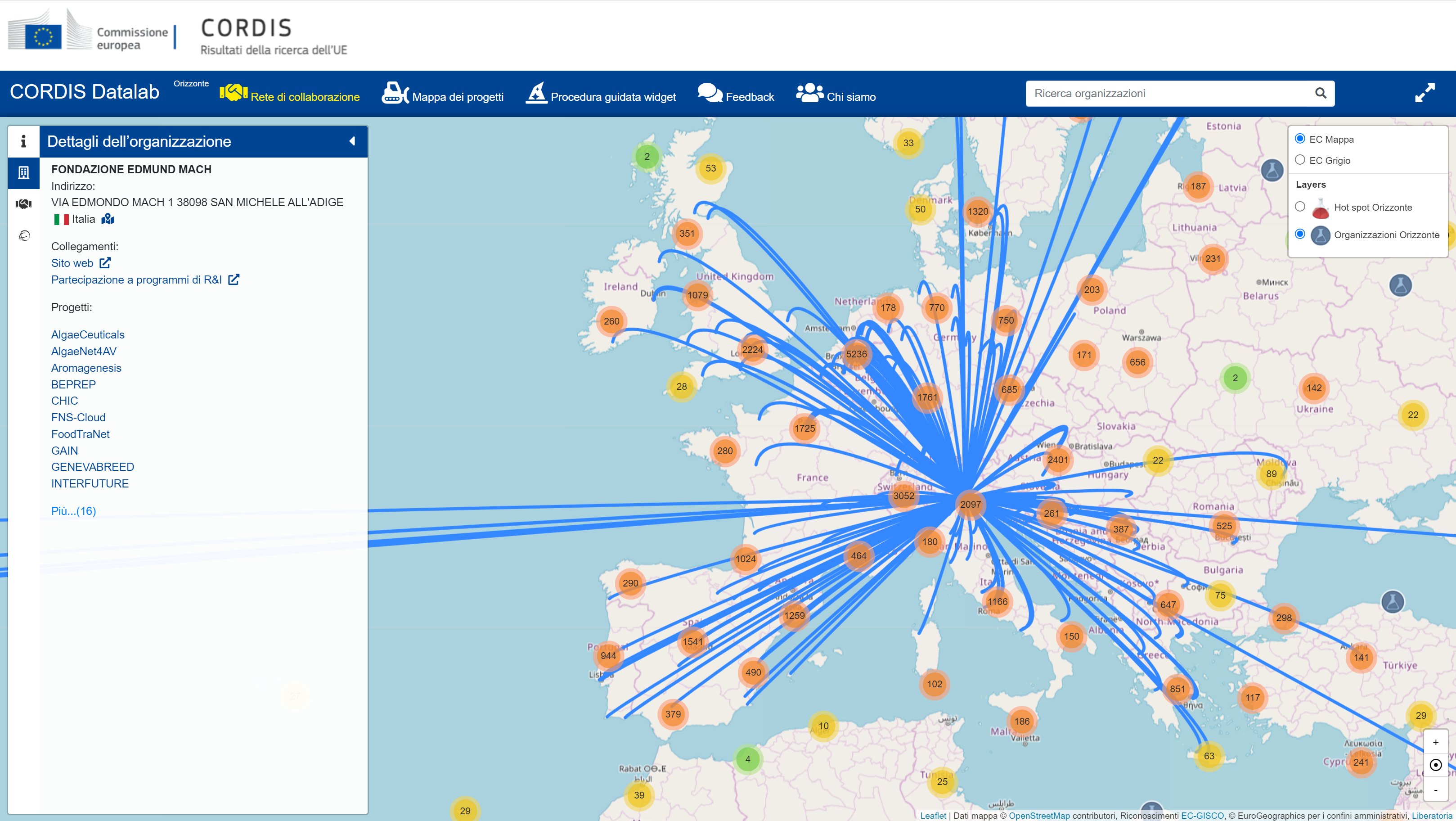
Source: CORDIS - European Commission
International financier
(EUPHRESCO) Il progetto mira a conoscere l'effettiva distribuzione geografica di D. bulgarica in Europa e a sviluppare metodi molecolari affidabili per la sua individuazione e identificazione. Ogni Paese partecipante raccoglierà dati sulla presenza di D. bulgarica nel proprio territorio, che saranno compilati per ottenere un modello di distribuzione più ampio del fungo in Europa.
Verrà sviluppato e convalidato un metodo basato sulla PCR per rilevare e identificare D. bulgarica e distinguerla dalle specie di Diplodia strettamente correlate o da altri membri della famiglia delle Botryosphaeriaceae che colpiscono mele e pere.
Attività FEM:
- Indagine sulla presenza di D. bulgarica;
- Caratterizzazione morfo-fisiologica e conservazione di isolati di D. bulgarica.
(OSF Inc.) The project is a collaborative project between the Okanagan Specialty Fruits Inc. [OSF], Canada and the foundation Edmund Mach. the project will have for objectives Project Objectives:
- Establish Protocols and processessprocesses leading to consistantconsistent regeneration of explants and/or plant tissues from single protoplast cells;
- Establish protocols and processes for reliable DNA-free transformation of single protoplstprotoplast cells by Gene Editing TechnolgiesTechnologies;
- Develop prototypes of fruit varieties (Apple, Cherry) with gene(s) of interest by following the protocols and processes established via objectives 1-2;
- Provide technical support for products developed via objective 3 leading to the commercialzation path for fruit varieties with novel traits.
(EUPHRESCO) - Il progetto ha lo scopo di creare un network internazionale di istituzioni e di esperti che valuti il rischio di invasione delle principali specie aliene negli agroecosistemi europei. Il consorzio si occuperà di mettere a punto modelli quantitativi per l'analisi prospettica (horizon scanning) al fine di identificare e prioritizzare i potenziali pest molto più rapidamente rispetto ai metodi tradizionali. La modellizzazione quantitativa sarà composta da diversi livelli, tra cui, ma non solo, la modellizzazione ecologica e la valutazione dell’idoneità climatica, tecniche di apprendimento automatico, distribuzione delle piante ospiti e criteri di valutazione rapida del rischio di introduzione ed insediamento.
L'obiettivo finale di questo progetto è la messa a punto di un kit di strumenti open-source e aggiornabile per condurre analisi prospettiche per la valutazione formale del rischio fitosanitario e la sorveglianza generale, applicabile a qualsiasi paese o regione di interesse, che possa essere direttamente integrato nelle attività normative.
Attività FEM:
La fondazione Mach verrà coinvolta nei seguenti work packages: WP2 - Dataset Identification and Sourcing, WP3 - Rapid Risk Assessment Criteria Identification e WP7 - Scientific publications
European financier
(EUSALP) The project aims to strengthen the governance and implementation capacity of EUSALP by improving coherence between the Revised Action Plan of the Strategy, the decisions of the General Assembly, and the 2026–2028 Action Group Work Plans. A key component is the reinforcement of the Secretariat, which will act as a strategic working unit delivering services to the Presidencies, the Executive Board, the Board of Action Group Leaders, their joint meetings, and the Action Groups, ensuring effective coordination across all levels.
(HEU Horizon Europe 21-27) To foster sustainable and efficient food production AgrifoodTEF empowers innovators with validation tools needed to bridge the gap between their brightest ideas and successful market products.
Built as a network of physical and digital facilities across Europe, the project provides services that help assess and validate third party AI and Robotics solutions in real-world conditions aiming to maximise impact from digitalisation of the agricultural sector.
The consortium of partners is composed of some of the major European players in the field of digital innovation applied to the agrifood industry.
Organized in three national nodes (Italy, Germany, France) and 4 satellite nodes (Poland, Belgium, Sweden and Austria), it offers its services to companies and developers from all over Europe who want to validate their robotics and artificial intelligence solutions for agribusiness under real-life conditions of use, speeding their transition to the market.

NRP Mission 4, Component 2, Investment 1.4 - Strengthening research structures and creating 'national R&D champions' on certain Key Enabling Technologies.
- MUR Notice No. 3138 of 16.12.2021
- Funding: 350 million euro (320 million from the PNRR)
- Directorial Decree of Granting of Funding No. 1032 of 17.06.2022
- Identification code: CN000022
- CUP: D43C22001220006

(Biodiversa+) Il progetto AirBiD, finanziato attraverso il partenariato europeo per la biodiversità Biodiversa+, si propone di investigare la composizione e la dinamica delle comunità aeromicrobiche e aeropalinologiche in ecosistemi urbani di diverse città europee. L'obiettivo primario è di caratterizzare la biodiversità dell'aria, analizzando la presenza e la distribuzione di bioaerosol (batteri, funghi, virus) e pollini, e di valutare il loro impatto sulla salute umana e sull'ambiente.
(Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions MSCA) This project seeks to exploit the microalgae biodiversity, as a source for high-added-value lectins and polyphenols with antiviral properties against influenza and coronavirus pandemic strains. Microalgae derived-compounds are easily amendable, bio-degradable, non-toxic and safe; thus, they are preferred to be used for the development of novel bio-based materials and cosmetics with antiviral potential. Lectins and polyphenols could be highly demanded non-drug interventions across the materials and cosmetics industry as a solution to reduce the risk and speed of contamination and transmission during pandemic outbreaks.
The project will combine the whole value chain in order to:
- develop transcriptomics and metabolomics resources from microalgae diversity as a valuable source for the discovery novel lectins and polyphenols;
- characterize their spectrum of bioactivity and toxicity and provide structure-function relationships;
- develop and optimize application-based microalgae culture systems and downstream processing strategies for higher production rate of the desired compounds;
- develop, formulate and evaluate lectins and polyphenols-based final cosmetics products.
The work will be supported by market assessment, integral biorefinery designs, techno-economic and sustainability assessment. Integrated value chains will be demonstrated to deliver proof-of-concept and demonstrate economic feasibility.
(HEU Horizon Europe) Preventing pandemics with biodiversity recovery.
How important is nature restoration targeting biodiversity recovery? Can it also help prevent future disease (zoonotic and vector-borne) outbreaks? Despite the thousands of ongoing and planned nature restoration projects globally, little is known about whether these restorations indeed interrupt the infect-shed-spill-spread cascade and mitigate disease risk. In this context, the EU-funded BEPREP project will find answers and provide practical information. Taking a participatory approach, BEPREP will involve indigenous and local communities in the identification of success factors of best practice restorations and interventions. The aim is to assist the infect-shed-spill-spread cascade and prevent disease outbreaks. BEPREP’s findings will contribute to shaping a Europe that is prepared to respond to disease risk.

Finanziamento nell’ambito del V bando dei Contratti di filiera
in ambito agroalimentare - MIPAAF AGRET 02 – Ricevuta Prot n. 0601443 del 23/11/2022
- Avviso MASAF 22 aprile 2022, n. 182458
- Finanziamento € 28.678.095,12
- Decreto Direttoriale di concessione del finanziamento MASAF N. 0308035 del 07/07/2025
- CUP B39I21001500001
I risultati del progetto saranno disponibili gratuitamente all'indirizzo https://sites.google.com/fmach.it/big/home a partire da gennaio 2029 per tutte le imprese attive nello specifico settore o comparto agricolo.
(biodiversa+) The main objective of the BIG_PICTURE project is to bring together the enormous amount of species data that is collected by the thousands of wildlife camera traps (automatic cameras) distributed across Europe by professional researchers, citizen scientists and other private individuals. By developing the appropriate electronic infrastructure (databases and artificial intelligence-driven image processing capability) and statistical tools for data analysis, the BIG_PICTURE project will facilitate the sharing, integration and joint analysis of data collected by many different institutions, allowing continental-scale assessments of species’ status.
EFSA - The BIODROB project focuses on the study of a xylem-feeding insect called Draculacephala robinsoni, a leafhopper recently introduced in Europe and suspected of being a vector of Xylella fastidiosa, a very dangerous plant bacterium.
The main goal is to gather detailed information about the biology, ecology, and behavior of this insect. Specifically, researchers will use advanced techniques, such as EPG (Electrical Penetration Graph), to closely observe how the insect feeds and how often it transmits the bacterium to different plants.
Furthermore, the project will analyze how these insects communicate with each other through vibrations. This research could lead to the development of "semiochemicals," that is, chemical or physical signals that attract or repel the insect, offering new strategies to control the spread of Xylella fastidiosa.
In summary, the BIODROB project aims to better understand a potential vector of a plant disease, with the goal of finding innovative solutions to protect our crops.
(HEU Horizon Europe 21-27) Bryophytes, including mosses and liverworts, have long been overlooked in the world of biotechnology. However, these ancient plants hold a treasure trove of biologically active compounds (BACs) with immense potential for bioeconomy. The BRYOMOLECULES project, a groundbreaking research initiative funded by the European Union within the Horizon Europe program, aims to explore and harness this potential, driving innovation in the cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries.
The BRYOMOLECULES project employs cutting-edge biotechnological approaches. By establishing innovative methods for cultivating bryophytes and engineering their metabolic pathways in controlled environments, the project aims to produce high-value BACs without relying on overharvesting natural populations. This dual strategy not only ensures a steady supply of these valuable compounds but also aligns with the European Union’s commitment to environmental sustainability and resource efficiency, paving the way for a greener, more sustainable bioeconomy.
Over the next three years, BRYOMOLECULES will provide groundbreaking insights into the vast untapped potential of European bryophytes, making significant contributions towards the European Green Deal, namely by:
- Advancing knowledge of European bryophytes and how they can be used in bioeconomic development, particularly in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical sectors;
- Developing innovative biotechnological methods to produce BACs, enabling new, greener biochemical routes that contribute to decreasing environmental impact;
- Driving economic growth by creating new, marketable, and patentable bio-based innovations that will support the development of sustainable industries in Europe, contributing to the circular economy;
- Engaging the public through educational initiatives to raise awareness about the ecological and economic value of bryophytes;
- Promoting the valorisation of the biotechnological capacity of European bryophytes by providing alternative methods for producing BACs, and at the same time reducing the pressure on natural populations by promoting conservation and preventing biodiversity loss;
- Active collaboration between academic and industrial partners, enhancing the competitiveness of European biotech companies and BAC producers. This collaborative approach will drive innovation and ensure that Europe remains at the forefront of bioeconomic development.
The ultimate goal of the BRYOMOLECULES project is to unlock the biotechnological potential of European bryophytes and support a transition to a greener, more sustainable economy.
(EU COST Action) The ability of forests to continue mitigating climate change depends on their ability to cope and adapt to global change drivers, such as more frequent climate extreme events and changes in atmospheric pollutants (namely carbon dioxide, reactive nitrogen and sulphur compounds). Different global change drivers could play a synergistic, antagonistic or predisposing role in affecting forest ecosystem functioning and health. All these drivers, however, are generally considered in isolation, and their effects on key processes (at tree, soil and ecosystem levels) are investigated separately in natural, periurban and urban forests, thus leading to uneven, un-coordinated and scattered information among different research communities. Without taking a holistic view on forest’s responses to global change, the future trajectory of Europe’s forests and their climate change mitigation potential can be fundamentally mis-assessed. CLEANFOREST will establish an inclusive and multidisciplinary pan-European network, which capitalizes on existing expertise and infrastructures (monitoring networks, manipulation experiments) to i) coordinate research efforts (e.g. data collection), ii) compare approaches and define common protocols to standardize measurements and methods used in global change studies, and iii) foster collaboration among different research groups to exchange and synthesize data, thus contributing to advancing scientific knowledge, identifying research gaps and providing suggestions for the next generation manipulation experiments and monitoring networks. Finally, CLEANFORST will benefit from the participation of key stakeholders (policymakers, small companies developing low-cost and effective instruments for environmental monitoring, citizen associations), by promoting mutual synergies to fulfil the urgent need of evidence-based solutions to policy, societal and technological challenges.
Action keywords
Forest functioning - Tree mortality - Manipulation experiments - Monitoring network - Global change driver interactions
(EU COST Action) In vitro culture of woody plants is leaving the academic laboratories and is now being developed in a range of commercial applications in horticulture and forestry that respond to the challenges of climate change and changing global food and wood consumption habits. It is therefore urgent that the research challenges, public acceptance, risk assessment and commercial application are confronted now in order to establish a well informed scientific community, policy makers and market place. This proposal concerns the following challenges, whose solution will have a significant scientific, social and economic impact: How can we overcome recalcitrance in a lot of woody plants? What are the best tools for diagnosis, sanitation and storing clean stocks? How can the production of elite clones be scaled up at a acceptable price? What are the real risks of this technology and how can the public be informed so that they appreciate and accept the applications ? How can foresters and landowners be persuaded to invest in planting poly-clonal forests? Taking these aspects into account, it seems more than urgent to us to set up a European network to connect the researchers involved from various domains, so that they can share innovations and develop new research strategies, assess the risks of the technology and improve communication with stakeholders and the general public.
FEM Activities: Contribution to WG2 (Diagnosis, sanitation and conservation) and WG5 (Communication, dissemination and technology transfer)
(ALPINE SPACE 2021-2027) Alpine lakes are facing anthropogenic challenges led by touristic pressures and eutrophication, worsening over time with climate change. Frequent cyanobacterial and algal blooms caused by eutrophication make waters unsuitable for drinking, recreation, and industry. Blooms are accompanied by decreased biodiversity and oxygen depletion, posing a risk to water ecosystem; cyanotoxins in blooms pose also a health risk. The challenges mentioned above can be addressed using novel satellite-based solutions and improved cooperation between academia and decisionmakers.
The project objective is to improve freshwater management, using novel ecosystem-based approaches for climate change adaptation and disaster risk prevention.

PNRR - Misura M2C1 I3.4 fondi Next Generation EU - “EVO-I.E.S. ITALIANO ECCELLENTE SOSTENIBILE”
- Avviso MASAF 22 aprile 2022, n. 182458
- Finanziamento € 18.145.591.96
- Decreto Direttoriale di concessione del finanziamento MASAF N. 0345799 del 25 luglio 2025
- CUP ......
(PNRR) Obiettivo del progetto di filiera è migliorare il controllo della qualità e della rintracciabilità dell’olio extra vergine d'oliva a supporto della sostenibilità ambientale.
Attività FEM:
Rintracciabilità geografica e varietale dell’olio EVO mediante tecniche NMR ed IRMS, e valutazione dell’efficienza dell’utilizzo dell’acqua di cultivar tradizionali italiane mediante analisi IRMS.
(EFI) FlyForSIF will combine hyperspectral and solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence airborne measurements to determine tree stress responses along a stress severity axis, to upscale current and possible future climate impacts on forests.
Extreme events in Europe have been shown to affect forest health status and they will likely increase in frequency, causing significant impacts. Super-sites integrating long-term ground observations and multi- scale spectral information need to be established across biogeographical regions, focusing on key forest types that have already shown significant degradation (such as evergreen and deciduous oak forests, and southern European pine forests). In this context, the FlyFor will combine hyperspectral and solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence airborne measurements to determine tree stress responses along a stress severity axis, to upscale current and possible future climate impacts on forests.
A biogeographical west-European transect including three super-sites (in forest ecosystems which are showing mild to severe signs of decline) was designed including:
- Mediterranean evergreen oak forests,
- continental deciduous oak forests,
- ow altitude alpine pine forests.
Ground-truth data available at the selected super sites (Eddy Covariance, defoliation, sap flow, canopy hyperspectral reflectance and SIF) will be integrated with additional FlyForSIF measurements (airborne SIF, Leaf Area Index, Leaf Water Content, Specific Leaf Area, leaf pigment content and leaf Pulse-Amplitude- Modulation-PAM fluorescence). Pigments (including xanthophylls) will be measured at selected trees during the summer of 2025. Flight campaigns will be carried out with IBIS-CASI-SASI hyperspectral sensors. The ability of single-tree spectral information to detect tree stress will be tested and upscaled to the satellite level using PlanetScope imagery.
In the FORWARDS initiative context, the expected results will act as a proof of concept for the future implementation of a multi-scale tool for long-term detection of climate change impacts on European forests. europee.
FEM activity:
- Project coordination
- Acquisition of hyperspectral images and processing
- Support on ground measuremnts at the Bosco della Fontana site
(HORIZON EUROPE 21-27 The project will focus on crop relatives of Rosaceae fruit tree species with the goal
- to enhance our knowledge onto the wild germplasm that is available Europe-wide either in-situ or in gene-banks as well as capturing local knowledge on the historical use and behavior of CWRs;
- to characterize this valuable plant material, phenotypically and genetically;
- to develop up-to-date methods of selection and genomic prediction adapted to the use of CWR in breeding programs.
FEM activities:
- - coordinate the workpackage "HTP genotyping of CWR core-collections and Information systems and tools for data management, integration, analysis and sharing";
- - coordinate the sampling of different Malus sylvestris populations in Italy and will host an ex-situ collection;
- - collaborate on developing new breeding strategies adapted to the use of CWR as breeding parents, combining marker assisted introgression for traits of interest (resilience, resistance to pests and pathogens, nutritional and fruit quality traits) with genomic prediction.
(Fondi EU Nazionali - Biodiversa+) Testare l'uso di un nuovo gruppo di indicatori della diversità genetica nell'ambito di specie prioritarie della Direttiva Habitat
Attività FEM:
Raccolta di dati di diversità genetica su specie italiane secondo le modalità condivise del progetto
(HEU Horizon Europe 21-27) - This project aims to develop disease-resistant grapevine varieties that are adapted to local environmental and pedoclimatic conditions to reduce reliance on chemical pesticides. It will also study consumer perceptions of the new resistant varieties and their resulting wines, which remain less familiar than traditional varieties. The project will also provide farmers, winegrowers and advisers with best practices and guidelines for integrated pest management in order to promote more environmentally friendly and sustainable viticulture in Europe.
The project has five objectives:
- Co-design a shared approach with stakeholders along the value chain in different European regions
- Lead in-depth research for a better understanding of the molecular basis behind vulnerability and resistance of grapevine to pathogens and how it interacts with its environment
- Develop traditional breeding programmes for new disease-resistant varieties in partnership with local stakeholders
- Lead research to develop emblematic varieties that maintain traditional characteristics in wine but are also disease resistant
- Design and share decision-making tools and best practices to optimise growing practices adapted to resistant varieties.

PNRR Missione 2 (M2) Rivoluzione verde e transizione ecologica, Componente 2, Investimento 3.5 - Ricerca e sviluppo sull'idrogeno, Programma RepowerEU
- Avviso MITE (ora MASE) 23 marzo 2022, n. 4
- Finanziamento: € 1.325.066,00
- Durata: 01/06/2025-30/06/2026
(PNRR) Sviluppo di un metodo analitico basato sull'analisi dei rapporto degli isotopi stabili dell'idrogeno per la rintracciabilità dell'idrogeno (da fonti rinnovabili o da combustibili fossili) come potenziale metodo complementare di certificazione del prodotto.
Attività FEM:
Analisi isotopiche rapporto isotopico idrogeno (Unità Tracciabilità), produzione di idrogeno da biomasse (Unità Bioeconomia)

NRP Mission 4, Component 2, Investment 1.5 - Creation and strengthening of 'Innovation Ecosystems', building 'territorial R&D leaders'
- MUR Notice No. 3277 of 30.12.2021
- Financing: € 109,866,032.00
- Directorial Decree Granting Funding No. 1058 of 23 June 2022
- Identification code: ECS000043
- CUP: D43C22001370006

(HEU Horizon Europe 21-27) The East Asian mosquitoes species Aedes albopictus and Ae. koreicus are invading several European countries, posing an increasing threat to human and animal public health. The life cycle of mosquitoes is strongly driven by temperature, making feasible the implementation of mathematical models predicting their distribution, population dynamics, and arbovirus transmission risk to support mosquito and Mosquito-Borne Viral Diseases management and control actions. However, the model's forecast reliability and biological realism are limited by the quantity and quality of the life-history traits observations used to inform the population dynamic model. This information is collected throughout laboratory experiments trying to assess the influence of temperature on different life-history traits (e.g., temperature-dependent adult mortality rate). Nevertheless, the results have been so far highly variable, due to i) different experimental settings and ii) multiple geographic origin of the biological specimens.
IFTAMED aims to review the current knowledge on the influence of temperature on the life-history traits of Ae. albopictus and Ae. koreicus, two invasive Aedes species of medical interest with established populations in North-East Italy, and implement it by designing targeted laboratory experiments under fluctuating temperature regimes, a laboratory setting that more accurately reflect variable environmental conditions in the field but not frequently applied in mosquito thermal biology experiments. The information collected from the review and the laboratory experiments will be disseminated in open-access databases and used to inform a population-dynamic mechanistic model, whose spatial and temporal forecasts will be integrated into an online early-warning system displaying information of practical interest (e.g, the estimated abundance of each life stage) for proactive mosquito control and management actions.
COST ACTION - INTUF aims to assess and compare urban forests in an integrated way, to develop reference frameworks for long-term, science-based strategic management and to stimulate administration through partnership building. FEM integrates the management aspects of urban greenery with a vision that aims to safeguard human health, promoting the on the species-specific study of the emission of allergenic pollen into the atmosphere and on intra- and inter-annual variations.
FEM participants: The Environmental Botany Unit participates in WG1, WG2 and WG4
(LIFE+) This project focuses on the adaptation of forest areas to extreme meteorological events, the promotion of fast responses to negative effects produced by such events, the acceleration of natural regeneration processes, targeting stable ecosystems with high biodiversity levels, and the generation of economic benefits to compensate the loss of income from timber exploitation.
Specific objectives are to:
- Consolidate the knowledge base on the use of innovative agroforestry procedures in forest farming, assess the effectiveness of the method and encourage its use in European forests;
- Develop an ecosystem-based innovative approach by implementing temporary/transitional (15/20 years) agroforestry until the growth of forest trees, and finalised to: i) tackle in the short time most of the negative effects caused to the environment by the destruction of trees (e.g. erosion, mineralisation of organic matter, loss of biodiversity); ii) accelerate the reconstruction of forest ecosystems, mixing natural and artificial reforestation concepts to promote the establishment of stable ecosystems characterised by high biodiversity and ecological value; and iii) create opportunities for sustainable economic development aiming to halt depopulation in the affected areas;
- Test and apply the VAIA approach in several areas characterised by different conditions to define fast response models to be transferred to other sites affected by extreme weather events, intensified by climate changes; and
- Promote the implementation of the EU Forest Strategy (in particular the 2021 Strategy).
The project contributes to the implementation of the EU Strategy on adaptation to climate change (COM(213)2016 and the new Strategy COM/2021/82 final); and the new EU Forest Strategy, under the European Green Deal, which highlights the need “to maintain and enhance forest resilience and adaptive capacity, including through adaptive solutions”. In addition, the project is in line with the 2019 Alpine Convention on climate change.
(EUREGIO) With more than 4000 vascular plant species, the Alps are one of the hotspots of European biodiversity. Particularly the Alpine grasslands are extraordinarily species-rich and harbour much of the biodiversity of the Alps. Polyploidisation (multiplication of chromosome sets) has been an important mechanism contributing to diversification of Alpine plants, also in the graminoid genus Luzula (Juncaceae). Contrary to true polyploidy, which is widespread across the plant kingdom, the process named agmatoploidy, i.e. fission of holocentric chromosomes, is restricted to a small number of plant families and genera, including Luzula. Compared to the multitude of studies dedicated to polyploid evolution, only a few studies have tackled diversification mechanisms of agmatoploids and our goal is to fill this gap by studying evolution and diversification of eight Luzula species in the Eastern Alps.
(COST OPEN CALL 2021) Mountainous areas are characterized by disparity, poorer territorial cohesion, unbalanced use and conservation of ecosystem services, rich and exploited natural resources, and marginalization.
MARGISTAR forum reflects collaboratively on natural, environmental, social and economic inter-relationships and
interactions in mountainous areas, and identifies a range of environmental, social, economic, and political
challenges.
It enables innovation through a range of physical and virtual meetings to co-design innovative
pathways for the transformation of marginalized mountainous areas towards their green, digital and healthy
futures.
(EU HORIZON) The project MICROBES-4-CLIMATE will provide a wider community of users/researchers, irrespective of location, efficient access to a cluster of complementary world-class Research Infrastructures and their integrated, advanced services along with training and scientific and/or technical support, to address such need. An excellence-driven programme of Transnational Access, which is at the core of the project, will enable users to conduct curiosity-driven research addressing terrestrial biodiversity and ecosystems, in light of the abovementioned multidimensional and still poorly understood microbiomes-plants-soil-environment interactions, and its roles in CG responses, resilience, and mitigation. This will foster the advancement of frontier knowledge and also pave the way to applied research on harnessing plant-microbiome interactions to improve the climate resiliency of plants/crops and to enable e.g., precision, sustainable and resilient agriculture.
(HEU Horizon Europe 21-27) Green extraction techniques for valorization of bioactive compounds from plant derived by-products. Nanoencapsulation for sensitive skin cosmetics production.
General objectives of the project:
- exchange of knowledge on bioactive compound properties,
- optimization of green extraction processes of such compounds from plant by-product materials,
- creation of innovative nanoencapsulated biocomponents for cosmetics formulations, mainly targeted on human sensitive skins.
FEM activities:
- phytochemical characterization of plant material and by-products
- extraction of natural compounds
- cultivation and provision of by-products

NRP Mission 4, Component 2, Investment 1.4 - Strengthening research structures and creating 'national R&D champions' on certain Key Enabling Technologies.
- MUR Notice No. 3138 of 16.12.2021
- Funding: 350 million euro (320 million from the PNRR)
- Directorial Decree of Granting of Funding No. 1032 of 17.06.2022
- Identification code: Progetto CN_00000033
- CUP: D43C22001280006

(HEU Horizon Europe 21-27) Today’s Earth observation (EO) data provides fast complex information concerning various changes on Earth. Could we use this data to protect our planet? The EU-funded OEMC project will provide the open-Earth-monitor cyberinfrastructure to accelerate Europe’s capability to process high-quality, user-friendly, environmental information, based on Earth observation (EO) data. The developed cyber-infrastructure will be secured in FAIR data principles and existing platforms related to EO will be leveraged to a higher level. This will allow the monitoring of essential biodiversity indicators and the registering of natural capital accounts for private and public sectors, allowing businesses to improve their competitive advantage through the EU Green Deal and European citizens to have a better quality of life.

PNRR Mission 4: Education and Research, Component 2: From Research to Enterprise, Investment 1.3 - Partnerships extended to universities, research centres, enterprises and research project funding:
- MUR Notice No. 341 of 15 March 2022
- Financing € 114,500,000.00
- Directorial Decree granting MUR No. 1550 of 11 October 2022
- Identification Code: PE0000003
- CUP B43C22000770006

(MUR) Il progetto riguarda lo sviluppo di processi innovativi per il pretrattamento, l’estrazione/separazione e successiva valorizzazione di scarti agroindustriali, utilizzando un approccio di bioraffineria a “cascata” per l’ottenimento di composti bioattivi (ad es. antiossidanti, polifenoli), chemicals/building blocks (acido lattico) e materiali (ad es. fibre high-tech, prodotti nutraceutici, PLA). Dai residui/sottoprodotti di trasformazione saranno ottenuti biocarburanti (biometano) e prodotti per l’agricoltura (ad es. ammendanti, biochar, biostimolanti). Sarà infine valutata la sostenibilità economica ed ambientale delle filiere individuate e verranno elaborati alcuni business case per i prodotti ottenuti.
(HEU Horizon Europe) Forests play a key role in the Earth climate system as they cover about 30% of the land area. In the last decade they absorbed more than 7 Gt of CO2 contributing to reduce global warming and to buffer and mitigate increasing climate variability. The summers of 2018 and 2019 included some of the hottest and driest periods ever recorded globally, however the extent and severity of their impact is unknown due to lack of a comprehensive monitoring network, which generally does not include hard-to-reach areas characterised by strong logistic limitations.
Therefore, novel technological solutions are urgently needed to monitor forest responses to climate change and related extreme events also in remote areas. Recent advances in Internet Of Things technology (IoT), satellite IoT connectivity and energy harvesting systems are opening unprecedented opportunities for the use of IoT devices in standalone experimental setups.
In this context, the aim of the RemoTrees project is to design and build an innovative, autonomous in-situ monitoring system designed for remote forest areas and providing data via satellite communication to a dedicated RemoTrees platform. In this framework, RemoTrees will integrate existing and novel Earth Observation (EO) data with in-situ observations of Essential Climate Variables (ECVs: fraction of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation, leaf area index, soil moisture, biomass change) and other key variables including e.g. stem growth, stem moisture, sap flow, canopy transmittance, besides air humidity and temperature. RemoTrees will include study cases on interoperability with GEOSS (Global Earth Observation System of Systems), and on how in-situ data can support an improved understanding of the climate variability impact on forests. The reinforced in-situ component will be beneficial for Copernicus products validation and will enhance the assessment of climate change long-term mitigation and adaptation potential of forests, towards novel insights for climate-smart forest management.
(HEU Horizon Europe 21-27) - The objective of SCALE-it is to increase the availability, accessibility and adoption of cost-effective alternatives to contentious inputs and thus reduce the dependency of organic farming on (a) critical plant protection products, (b) manure from conventional farms, (c) antibiotics and anthelmintics, and (d) synthetic and GMO derived vitamins.
(H2020) It aims to reduce food waste with sustainable innovations at all stages of the fresh food supply chain, to assess perceived food quality and consumer acceptance.
(FutureFoodS Call 2024) - The European Commission (EC) has identified an urgent need to make our food systems future-proof. This is due to various impacts that our food systems are facing and the need to safeguard our food cultural heritage.
SpeedyFermHub proposes the creation of an inter-disciplinary ‘Hub’ across Europe, that combines different facilities and know-how for the fast development and evaluation of new fermented food products and microorganisms. Ideally, the ‘Hub’ should include capabilities for fast technological / microbiological / sensory characterisation, adequately supported by facilities able to support fast transition of ‘new foods’ from lab to pilot scale. The different new food products developed during the Action, will provide ‘proof of principle’ of the Hub functionality.

National Recovery and Resilience Plan - Measure 1 Component 3 Intervention 2.1 “Attractiveness of historic villages Local Cultural and Social Regeneration Project”
- MUR Notice of December 20, 2021
- Financing: € 1.582.000,00
- Directorial Decree for the Concession of Loans n. 453 of 7 June 2022
- Identification code: CiG Z02392F795
- CUP: H18C22000030006
(Alpine Space 2021-2027) Mountain headwaters are a key component of Alpine water resources providing natural- and socio-ecosystem services. Climate change, with the degradation of the cryosphere (glaciers, permafrost, snow), and human pressure are increasingly impacting mountain headwaters availability and quality in Alpine systems. These alterations challenge Alpine communities and impact ecosystem services. The design of effective adaptation plans and management strategies remains a challenge for policy makers and stakeholders of Alpine territories, due to data gaps, difficulties to develop hydrological models enabling testing management scenarios and insufficient knowledge transfer from science to policy and from policy to science.
Thus, the WATERWISE project aims to provide solutions for communities and protected area managers to assess the vulnerability of headwater catchments and design sustainable management and adaptation strategies.
(MSCA) How human-made noise affects wildlife.
Human-made noise impacts wildlife populations by disrupting their natural soundscapes. Understanding how noise affects wildlife’s ecological niches is essential to protect biodiversity. With the support of the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions programme, the WildSOUND project investigates the impacts of human-made noise on wildlife in Alpine ecosystems, with a particular focus on mammals. The research aims to promote the sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems in alignment with UN SDG 15 and the Horizon Europe programme. Using an extensive array of acoustic recorders, it will measure sound levels and identify sources of anthropogenic noise. It will also assess the behavioural and physiological effects of anthropogenic noise on wildlife and conduct controlled experiments to provide comprehensive insights.
(Fondi EU Nazionali - Biodiversa+) Using multidisciplinary approaches, estimate the impact of hybridization between wolves and domestic dogs with a view to setting up better management and conservation activities for wolf populations.
FEM activities:
Population genomics analysis using Whole Genome Sequencing (at an internal sequencing platform) and bioinformatic analyses.
National financier
(contratto di Filiera) Obiettivo del contratto di filiera è la promozione della competitività e sostenibilità dell’acquacoltura di montagna
Attività FEM: genetica di conservazione del carpione; analisi e monitoraggio delle acque per garantire la qualità della risorsa idrica attraverso l'analisi del DNA ambientale; introduzione di sistemi di machine vision e modelli previsionali per l'adattamento ai cambiamenti climatici e per la riduzione dei fenomeni di overfeeding con conseguente riduzione degli spechi.
(ASI) The BIOMIRATE project aims to investigate and exploit DNA repair mechanisms found in extremophilic organisms to develop innovative strategies for mitigating ionizing radiation-induced damage. The primary objective is to identify and molecularly characterize DNA repair pathways in radiation-resistant organisms, with the intent of translating this knowledge into biotechnological applications for radioprotection and bioremediation.
(Bando ASI) Obiettivi generali del progetto: Caratterizzazione multi-omica di comunità endolitiche antartiche come potenziale modello della vita su Marte.
Attività FEM: Analisi metabolomica, integrazioni dati di metabolomica e metagenomica, predizione di funzioni metaboliche a partire da esperimenti di metagenomica shotgun

(MIUR PRIN) Il riscaldamento globale, oltre al degrado del territorio, diminuzione della resilienza e riduzione della qualità dell' acqua, favorisce anche la frequenza e la gravità degli incendi. Gli effetti degli incendi, oltre ad essere distruttivi sulla vegetazione, causano una alterazione dell'attività e dell’abbondanza microbica del suolo per anni e poco si sa riguardo alla gestione ed il recupero delle aree aride e semi-aride soggette a incendi.
Il presente progetto valutando l'effetto dell'incendio sulla vegetazione e sulle comunità microbiche prima e dopo l’evento su aree selezionate e periodicamente impattate, avrà l’obiettivo di valutare il ruolo delle successioni microbiche e vegetali nel recupero post-incendio.

(MIUR PRIN) Obiettivi generali del progetto sono lo studio degli effetti di insetticidi subletali sull'efficacia e la biologia comportamentale di Drosophila suzukii, di afidi fitofagi e dei loro parassitoidi specifici.
Attività FEM:
- Esperimenti nella struttura di Biotremologia per valutare il comportamento vibrazionale di D. suzukii sottoposta a dosi subletali di insetticida.
- Valutazione delle conseguenze sui parassitoidi in termini di variazioni comportamentali legati alla comunicazione vibrazionale di ricerca degli ospiti.
(Progetti di Ricerca Corrente 2024) Negli ultimi anni sono state sviluppate nuove tecniche di miglioramento genetico delle piante, incluse le tecniche di mutagenesi mirata genericamente chiamate "editing del genoma" (GE). Il sistema CRISPR/Cas9 è attualmente il più promettente per semplicità d’uso e per specificità. Nel sistema CRISPR/Cas9, infatti, il riconoscimento della sequenza di DNA da modificare è operata non da proteine, ma da una sequenza di RNA. Ad oggi, i soli sistemi analitici in grado di caratterizzare adeguatamente i prodotti di GE sono basati sul sequenziamento del DNA dell’organismo trasformato, operazione non proponibile in routine diagnostica per i costi ed i tempi di esecuzione elevati.
Questo progetto ha lo scopo di completare ed approfondire il lavoro svolto per la RC LT 07/20. In tale progetto è stata utilizzata la tecnica dell’High Resolution Melting (HRM), una metodica post qPCR, condotta in presenza di un fluoroforo che, intercalandosi nella doppia elica del DNA emette fluorescenza, permettendo di distinguere ampliconi con diversa sequenza, e quindi diversa temperatura di melting. Ciò consente di rilevare diverse varianti di sequenza del DNA come: cambiamenti di singola base, inserzioni, delezioni e duplicazioni. I protocolli analitici quali l'HRM sviluppati durante la RC LT 07/20 saranno ottimizzati, in collaborazione con la Fondazione Edmund Mach (FEM), con l’obiettivo di portare il protocollo di screening sviluppato per la rilevazione di linee editate di vite a discriminare le diverse linee editate in base al tipo di mutazione presente, ed al contempo di tentare l’applicazione del protocollo ad altre specie vegetali, tra le colture frutticole più coltivate nelle regioni temperate del mondo. La scelta sarà orientata tenendo conto dell’interesse dei consumatori e, dal punto di vista agronomico, delle nuove sfide poste dal cambiamento climatico che espone le colture tradizionali a nuovi stress biotici (insetti o agenti patogeni batterici, fungini e virali) ed abiotici (siccità, temperature, alterata composizione del terreno). Il progetto potrà selezionare le linee pilota, tra quelle trasformate presso la FEM mediante sistema CRISPR/Cas9, e sviluppare un metodo in PCR real-time con analisi HRM per la caratterizzazione delle linee editate prese in esame.

(MIUR PRIN) Gli obiettivi principali del progetto sono:
- Fornire una metodologia di contabilità completa per misurare il bilancio delle emissioni di carbonio e altri GHG considerando anche l'uso successivo di alcuni prodotti rilevanti per la contabilità C, come il legno.
- Sfruttare le nuove tecnologie IoT per monitorare in chiave continua processi ecosistemici che contribuiscono al bilancio netto C e GHG delle foreste e degli ecosistemi di colture legnose che consentono di creare un quadro di modellizzazione contabile sulla base di dati assimilati sul campo.
- Testare i prototipi contabili delle nuove soluzioni tecnologiche per la modellazione dei dati su 2 siti forestali e 2 frutteti.
- Fornire uno strumento operativo per il bilancio netto C e GHG nella silvicoltura e settore agroforestale per la scienza e le imprese.
Attività FEM:
Fem sarà coinvolta negli obiettivi 2 e 3 con un sito in foresta

(MIUR PRIN) Obiettivo generale del progetto è lo studio della co-evoluzione genomica della popolazione umana della Val Rendena e la razza bovina Rendena. Questo progetto è una continuazione della collaborazione a lungo termine sulla genomica della Razza Rendena con UNIPV e UNICATT (vedi progetto di dottorato RENDENAGEN).
Attività FEM:
Partecipazione all'interpretazione dei risultati dal punto di vista genomico, storico e antropologico; stesura pubblicazioni scientifiche; disseminazione dei risultati al pubblico.
(Fondi EU Nazionali - Biodiversa+) The project aims to form an international collaboration aimed at studying the biodiversity and ecosystem services associated with river riparian areas. Through the combination of remote-sensing and field data collection with coordinated approaches in the six study basins (Germany, Italy, Czech Rep., Sweden, Portugal), the results will contribute to the identification of riparian habitats with high conservation priority as hot- spot of diversity and key role as an ecological corridor. The project involves extensive dialogue with local and international stakeholders in order to guarantee the relevance of the results for the governance of conservation and management of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems aiming at the 2030 Biodiversity Strategy.
FEM activities:
The main FEM activities will be linked to sampling and metagenomic analyzes relating to the study of the microbiological component of soil, sediments and water. FEM will also play a key role in the analysis and statistical modeling of the entire ensemble of data collected in the field and remotely.
(Ministero della Salute) L’echinococcosi alveolare e le infezioni da Hantavirus sono zoonosi che costituiscono un serio problema sanitario in Europa. In entrambi i casi, si tratta di zoonosi gravi, con una letalità variabile ma non trascurabile. Ciò che le accomuna è il fatto che il loro ciclo biologico è legato ad alcuni piccoli roditori selvatici, che per Echinococcus multilocularis costituiscono gli ospiti intermedi e per Hantavirus il serbatoio naturale. La stretta relazione con tali specie, comuni ma tipicamente elusive e poco conosciute, rende complesso indagare la distribuzione e l’ecologia di questi patogeni, e a maggior ragione valutare il rischio di infezione per l’uomo. Risulta pertanto strategica un’indagine strutturata su questi ospiti, in particolare Apodemus flavicollis e Myodes glareolus, generalmente considerati il principale serbatoio per gli Hantavirus, e Arvicola amphibius, che recenti studi suggeriscono rilevante nell’eco-epidemiologia di E. multilocularis.
Attività FEM:
- WP4, Task 4.1: Genetica di popolazione di Arvicola amphibius anche in relazione alla presenza e prevalenza di E. multilocularis;
- WP1 Progettazione campionamento;
- WP3 Epidemiologia;
- WP5 Analisi del rischio.

(MIUR PRIN) Development of a transgene-free genome editing tool for clonally propagated fruit crop. We would like in this project (i) use and develop nanoparticles which transport across the plant cell membranes protein and DNA. (ii) Identify nanoparticles or nanobubbles that are highly efficient for plant cell internalization, and utilize these nanoparticles to deliver DNA, RNA, and Cas9-gRNA RNP to different plants tissue such as calli, somatic embryos, meristem or protoplast in a fruit tree species-independent manner.
FEM activity:
in vitro characterization of nanoparticule and nanobubble systems for the delivery of DNA and CRISPR/Cas9 machinery in apple
(TEA4IT) TEA4ITFund si propone come una piattaforma di ricerca avanzata, volta a generare nuove conoscenze scientifiche e sviluppare strumenti applicativi per l'impiego strategico delle Tecnologie di Evoluzione Assistita (TEA) nel settore agroalimentare.
In un contesto caratterizzato da cambiamenti climatici, crescente richiesta di prodotti agroalimentari di alta qualità e necessità di ridurre l'impatto ambientale dell'agricoltura, il progetto si fonda su un approccio multidisciplinare che integra biologia molecolare, genomica funzionale, bioinformatica, fisiologia vegetale e tecnologie innovative di genome editing.
(TEA4IT) TEA4IT‑Tree è il sottoprogetto dedicato alle specie arboree da frutto. Mira a sviluppare e ottimizzare protocolli TEA applicabili a colture perenni, caratterizzate da cicli lunghi e da una maggiore complessità nella rigenerazione e trasformazione.
Il sottoprogetto TEA4IT‑Tree si concentrerà sulla generazione di linee di melo e vite ottenute tramite tecnologie di genome editing senza integrazione stabile di DNA esogeno (DNA‑free edited plants).
(ANCI) Enhancement of abandoned/underused mid-mountain areas in the municipality of Arco - Alto Garda area in Trentino. The project activity is carried out in (in)formative moments or indications to the technical staff of the municipality or local stakeholders on specific activities in the livestock sector, such as the valorisation of meadows/pastures, minor crops /organic agriculture, enhancement of the beekeeping sector and restoration of chestnut trees. The main aim is the recovery of that part of the public heritage - which belongs directly or indirectly to the Municipality of Arco - currently in a state of decay/abandonment. In particular, these are terraced, hilly or high-altitude land allotments where there are also huts that the Municipality would like to analyze, in order to understand how to revitalize and consequently assign management to young farmers.
Local financier
Hub for the surveillance of vectors of public health relevance aimed at harmonizing the activities of various provincial offices monitoring of arthropod vector species (funded by: Province of Trento)
(ASSAM) Il progetto prevede la realizzazione di varietà resistenti a peronospora e oidio con l'incrocio con le varietà marchigiane Verdicchio, Pecorino e Montepulciano.
Attività FEM: Incrocio tra i genotipi di vitis vinifera Verdicchio, Pecorino e Montepulciano con i nostri genotipi piramidizzati con resistenze a oidio e peronospora.
(BIM Sarca, Micio, Garda) L’obiettivo generale del progetto è la valorizzazione e l’innovazione della filiera noce e della filiera castagno in maniera sostenibile.
Attività FEM:
- Intervento 1: la valutazione del processo di maturazione e dei tempi ottimali di raccolta del noce;
- Intervento 2: la caratterizzazione di due importanti patologie del noce, antracnosi e batteriosi, con valutazione di suscettibilità varietale;
- Intervento 3: la valutazione del fabbisogno idrico di un castagneto come base per lo sviluppo di un modello di gestione efficiente del castagneto;
- Intervento 4: la valutazione di una possibile riduzione degli sprechi di produzione e lavorazione con conseguente creazione di nuove opportunità per valorizzare al massimo le risorse locali.
(AdPi) Attività di collaborazione istituzionale Servizio faunistico PAT e FEM
Attività FEM:
Si distinguono due macro-attività principali, che vengono dettagliate come segue:
A. Programmazione progettuale piano faunistico: le attività prevedono l’individuazione delle priorità scientifiche di monitoraggio, ricerca e analisi, nonché lo sviluppo di disegni sperimentali, per rispondere agli obiettivi previsti dal Piano Faunistico 2025-2035. Nello specifico le attività sono relative a tre schede di indagine, che riguardano l'impatto del lupo sugli ungulati selvatici e valutazione dell’efficacia delle misure di prevenzione e difesa del bestiame domestico; lo status e distribuzione dello stambecco; il comportamento dell’orso in ambiente alpino
B. Ungulati ed investimenti stradali – soluzioni gestionali di mitigazione: il progetto prevede una valutazione delle aree nelle quali si concentrano gli investimenti stradali in funzione dell’abbondanza di selvatici, dell’intensità del traffico e di sistemi di dissuasione. In tale contesto, le attività richieste integrative a FEM includono lo sviluppo di modelli di intensità di uso di strade, densità di incidenti ed eventuale valutazione della connettività presso gli hotspot. FEM contribuirà inoltre alla valutazione demografica come attività già prevista in accordo di programma pluriennale.
(PAT) L'obiettivo principale del progetto è quello di sviluppare e implementare soluzioni innovative per la gestione della Flavescenza Dorata nei vigneti.
(ADP) Updating the Genetic Status of Populations of Various 'Minor' Fish Fauna Taxa.
Managing fish fauna in public waters is indisputably important for two main reasons: first, the conservation of endemic taxa, those at risk of extinction, or those crucial for the functioning of communities and ecosystems; second, the sustainable administration of fishing activities. Many management efforts and dedicated resources are therefore focused on species or taxa of primary importance for conservation (as listed in the Habitat Directive annexes and IUCN Red Lists) or those that are a primary target for the fishing community. The most striking example in the Alpine region is the marble trout, which undoubtedly receives the maximum effort—both in terms of activities and finances—for its management.
However, adequate attention, albeit on a smaller scale, should also be given to species and taxa of more limited interest for fishing or those considered at lower risk. This is often due to a real lack of adequate knowledge rather than an actual healthy state of the populations. These populations play a fundamental role in ecosystems, a role that deserves to be protected through appropriate management practices and enhanced through relevant research and study activities.
(AdPi) L'obiettivo del progetto è una migliore conoscenza delle conseguenze sui popolamenti forestali delle infestazioni di bostrico e di una migliore programmazione degli interventi di ripristino.
(AdPi) Obiettivi generali del progetto:
(A1) - Aggiornamento dello stato genetico delle popolazioni di Trota marmorata ascrivibili ai principali corsi d’acqua alpini Veneti, analizzando sia esemplari già in allevamento presso impianti che individui allo stato selvatico, questi ultimi reperibili nel corso dei monitoraggi che Enti pubblici dovessero programmare in collaborazione con le locali Associazioni di pesca sportiva.
(A2) - Sviluppo e diffusione dei protocolli per una gestione su base genetica della riproduzione della Trota marmorata nelle strutture ittiogeniche del Veneto finalizzata alla produzione del miglior materiale da ripopolamento per le acque pubbliche.
Attività FEM:
• Amministrazione generale del progetto per la Fondazione E. Mach – A1, A2
• Partecipazione al coordinamento tecnico del progetto – A1, A2
• Partecipazione alle attività di marcatura fisica e prelievo dei tessuti – A1
• Estrazione del DNA – A1
• Analisi genetiche – A1
• Elaborazione dei dati genetici e delle analisi biostatistiche – A1
• Elaborazione di relazioni tecniche – A1, A2
• Redazione del protocollo di riproduzione – A2
• Partecipazione alla divulgazione e comunicazione dei risultati – A1, A2
• Redazione pubblicazioni scientifiche (con possibile coinvolgimento di altri partner)
(AdPi) La collaborazione consiste nella continuazione dell'attività di monitoraggio genetico ed analisi dati delle popolazioni di orso (Ursus arctos), di lupo (Canis lupus) e di gallo cedrone (Tetrao urogallus) sul tutto il territorio provinciale in stretta collaborazione con i tecnici del Servizio Faunistico e Servizio Foreste PAT e con ISPRA. Gli obiettivi saranno conseguiti attraverso la tipizzazione genetica individuale di campioni non invasivi (escrementi, saliva, urina, peli, piuma).
(AdPi) Introduzione di un approccio innovativo ad un’irrigazione più precisa e puntuale.
Attività FEM:
Definizione del contesto operativo, sviluppo del modello SWAB e setup ed esecuzione della sperimentazione nei siti pilota
(AdPi) Predisporre una metodica uniforme per le analisi genetiche, allo scopo di consentire una descrizione transazionale della popolazione dei lupi della regione alpina. Sarà creato un database per garantire lo scambio dei dati relativi ai lupi genotipizzati, tra le diverse regioni ArgeAlp, come dettagliato nella resoluzione della COmunità di lavoro delle Regioni Alpine (ARGEALP) su tema della "Gestione transfrontaliera del lupo" adottata dalla 53a Conferenza dei Capi di Governo di ArgeAlp il 21 ottobre 2022 a Innsbruck.
ATTIVITA' FEM:
Ottimizzazione di un metodo di high throughput sequencing per la genotipizzazione dei campioni non-invasivi di lupo nelle regioni ArgeAlp Italia, in collaborazione con gli altri 3 laboratori incaricati dalle regioni ArgeAlp delle analisi dei campioni di lupo: Research Institute of Wildlife Ecology (Austria), Senkenburg Institute (Germania), e Univ. Lausanne (Svizzera). Parteciperà alla creazione di un database transnazionale per garantire lo scambio efficiente dei dati relativi ai lupi genotipizzati tra le diverse regioni di ArleAlp.
Marble trout conservation, hybridization, supplemental breeding
(AdPi) Aggiornamento dello stato genetico delle popolazioni di Trota marmorata nei principali bacini trentini. Supporto genetico alle attività di riproduzione della Trota marmorata nelle strutture ittiogeniche gestite dalle Associazioni di Pesca sportiva. Monitoraggio genetico di altre specie di interesse conservazionistico: trota lacustre (Salmo trutta complex), temolo adriatico (Thymallus aeliani) e luccio italico (Esox cisalpinus).
Attività FEM:
• Partecipazione alle attività di marcatura fisica e prelievo dei tessuti
• Estrazione del DNA
• Analisi genetiche
• Elaborazione dei dati genetici e delle analisi biostatistiche
• Elaborazione di relazioni tecniche
(PSR PAT 2023-2027) Il progetto prevede di rilevare in diversi ambienti trentini il comportamento di alcune delle varietà resistenti iscritte da parte di CIVIT nel 2020 al RNVV, quelle che hanno cominciato l’iter di protezione e registrazione nel 2024 e alcune molto promettenti, in fase di sperimentazione,sviluppando i caratteri enologici che possono individuare tipologie di vinificazione adatti alla migliore valorizzazione delle varietà, in particolare sulla spumantizzazione.
(AdPi) The SWAT3 project, conducted at the Edmund Mach Foundation, focuses on classical biological control, a sustainable approach to managing two invasive insect pests: the Asian brown marmorated stink bug and the spotted wing drosophila.
Closed projects (since 2024)
(Fondazione VRT) Sviluppo di procedure di Intelligenza Artificiale per l'identificazione di tracce audio in ambiente antropico e naturale, in particolare per l'estrrazione della banda di tecnofonia (rumore di origine antropica indiretta) e geofonia (rumore bianco da eventi naturali).
Attività FEM: concettualizzazione del design sperimentale; coordinamento di progetto; test in ambiente; contributo ad attività di divulgazione.
(EU COST ACTION) Bioaerosols are among the most complex components in the atmosphere. Bioaerosols are relevant as important pathogens in crops and on trees, as aeroallergens in relation to human health and as catalysts for physical processes in relation to climate such as cloud formation processes. For decades the backbone in the European monitoring network of bioaerosols in relation to crop and human health has been simple impactors that trap the bioaerosols on a sticky surface followed by optical identification using microscopes. This approach is both time consuming, expensive and limiting with respect to the progress of science. The last five to ten years a range of new techniques have become available that enable a number of scientific breakthroughs in the general understanding of bioaerosols and how they interact with the environment. This COST action will establish an interdisciplinary network of experts currently involved in the detection of bioaerosols using both existing methods as well as upcoming technologies such as real or near real-time technologies from atmospheric chemistry and physics or eDNA methods used in molecular biology. A main objective is to critically address the barriers that limits the penetration of new methods in detection of bioaerosols. The cost action will stimulate both research and technological development, e.g. by developing approaches for integration of multiple methods for detecting bioaerosols and how to handle data using numerical approaches in a big data environment by using fungal spores and pollen as examples.
(SPP) Lo scopo del programma di cooperazione fra FEM e CIVIT è quello di applicare le tecnologie di evoluzione assistita (TEA) e di rigenerazione da protoplasti, sviluppate da FEM negli ultimi anni nell’ambito del progetto Chardonnay +, a varietà di uva da vino di interesse per la viticoltura Trentina e nazionale ottenendo prototipi migliorativi di materiale clonale vegetale da sottoporre a valutazione per eventuale sfruttamento commerciale. I caratteri migliorativi che si intende introdurre in queste varietà sono la resistenza/tolleranza a peronospora e oidio e se possibile ad entrambe le malattie.
Attività FEM:
WP1: produzione di callo embriogenico
WP2: Ottenimento di protoplasti
WP3: Gene Editing dei protoplasti
WP4: Rigenerazione di piante a partire dai protoplasti trasformati con RNPs
WP5: Analisi molecolare e fenotipica delle piante editate
The main objectives of EYWA lie with the need to offer a scalable, reliable, sustainable and cost-effective Early Warning System (EWS) relying on big Earth Observation (EO) data in conjunction with environmental, climatic and meteorological essential parameters, socioeconomic and population data, ecosystem and morphological related parameters, as well as epidemiological and entomological data to forecast and monitor MBDs.
(H2020 MSCA-ITN-2020) Food quality, safety and security training for early-stage researchers.
The rapidly growing and changing nature of food science means researchers require a multidisciplinary, intersectoral understanding of mass spectrometry to successfully exploit both traditional and state-of-the-art methodologies and techniques. The FoodTraNet project will address this challenge by providing training to high achieving early-stage researchers (ESRs) via a common platform of advanced mass spectrometry tools for food quality, safety and security. A multidisciplinary training and research network will be created to give ESRs the opportunity to transfer their knowledge from scientific to industrial applications. FoodTraNet will cover techniques including stable isotopes, target, suspect, non-target screening, and mass spectrometry imaging to identify biomarkers and bioactive compounds to ensure food quality and traceability.
(WELLCOME FOUNDATION) General objectives of the project: to establish an innovative and multidisciplinary research group to develop analytical methods capable of identifying drugs subject to fraud (falsified and substandard (SF) medicines) with a particular focus on antimicrobials.
FEM activity: use of the analysis of stable isotope ratios as a potential method for determining drugs subject to fraud similar to what is already done in the agro-food sector.

National Recovery and Resilience Plan - Measure 2 Component 1 Intervention 3.2 “Green Communities”
PdCM – DARA notice of 30 june 2022
- Financing: € 4.716.000,00
- Decree for the Concession of Loans n. 15691 of 28 september 2022
- Identification code: CiG A03601D78F
- CUP: H37F22000010006
(EIT Food-KIC) Assessing digital and cultural potential of Food Hubs towards sustainable local food systems.
This project aims to study and test the importance of designing sustaining and managing landscape and social infrastructure to make food circular sustainability more shared and practicable. The shortening of the supply chain could be a solution to improve the economic, social and environmental sustainability of the food supply chain. To promote these changes, it is necessary to work with a multiscale and multilevel approach. The project aims to explore agroecological landscapes as places for social innovation, care and transformation in support of sustainable local food policies in RIS countries (Italy, Spain, Portugal).
The project explores the role of food as an element of reconnection between farmers, citizens and “eaters” (i.e. citizens more aware of sustainable food issues) through the promotion of Community-Supported Agriculture models as sustainable examples of production, distribution, and consumption of food as well as care and enhancement of the landscape.
(MASAF) Obiettivi generali del progetto sono l'aggiornamento delle banche dati isotopiche ufficiali di vino/mosto ed olio d'oliva e lo sviluppo di nuovi metodi per il controllo dell'autenticità dei prodotti agroalimentari.
Attività FEM:
- analisi isotopiche secondo metodi ufficiali,
- supporto tecnico-scientifico a ICQRF-MIPAAF,
- sviluppo nuovi metodi analitici per la tracciabilità dei prodotti della filiera agro-alimentare.
(HORIZON 2020) The IMPETUS project aims at accelerating Europe’s climate change response and turning commitments into concrete action, developing innovative measures to make its regions more resilient. Moreover, the project explores the synergies between climate change mitigation, supporting regional socio-economic growth and stability, and transition of communities to ecological sustainability and resilience.
IMPETUS develops and validates a coherent multi-scale, multi-level, cross-sectoral climate change adaptation framework to accelerate the transition towards a climate-neutral and sustainable economy. IMPETUS Resilience Knowledge Boosters (RKBs) build a robust Quintuple Helix stakeholders' community (human dimension) complemented with reliable data and assessment methods to support decision and policy making (digital dimension). This results in community empowerment to co-design, assess, deploy, and monitor climate adaptation Innovation Packages, including R&I methodological, technological, governance, awareness, behavioural, economic, financial and pathway components.
IMPETUS RKBs is deployed and validated in all 7 EU biogeographical regions (Continental, Coastal, Mediterranean, Atlantic, Arctic, Boreal, Mountainous) covering all Key Community Systems, climate threats, and multi-level governance.
(AdPi) Monitoraggio genetico del lupo nell'ambito del progetto europeo LIFE WOLFALPS EU-LIFE18 NAT/IT/000972: “AZIONI COORDINATE PER MIGLIORARE LA COESISTENZA LUPO-UOMO NELL’AREALE ALPINO"
(H2020) Innovative models, tools and services for early detection and monitoring of emerging disease to increase the operational capabilities of EU public health.
(EU ERA TALENT) FEM, as an EURAXESS Local Point, is committed to promoting the development of careers and the mobility of researchers. The project "Mentoring Routes: Unleashing Innovative Careers for Young Researchers (MR2YR)" pursues this goal by aligning with the ERA Talents action, which aims to improve the interoperability of careers and the employability of talents in the field of research and innovation across various sectors.
The project offers a training program dedicated to young researchers and PhD students, including workshops, meetings, and seminars led by experts. It focuses on enhancing research through the drafting of project proposals, strategies for communicating the impact and results of research, and entrepreneurship.
The aim is to support young researchers and doctoral students in shaping their future and exploring new career opportunities beyond traditional academic paths, while bridging the gap between their current research activities and future aspirations. It also aims at linking research with society by encouraging young researchers to realize the true potential of their work and facilitating their transition from academic to non-academic careers. This action is in line with the objectives of the Researcher Careers Beyond Academia Hub, a network of EURAXESS members aiming to support early career researchers in their transition to non-academic careers and to establish a network of local actors bridging the gap between research and socio-economic sectors. The training path will be designed and implemented in collaboration with the Trentino Innovation Hub Foundation (HIT).
It will also extend the EURAXESS services already provided by the FEM, including a Welcome Office to support international mobility and initiatives to improve the support and follow-up of research careers.
(Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions MSCA) Understanding role of neuroactive compounds in the diet in the development of neurodegenerative diseases.
Growing evidence points to the links between diet, gut, and neurodegenerative diseases (ND). Funded by the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions programme, the NeuroTOm project aims to understand the significance of exposure to neuroactive compounds in the diet. Using tomato as a food source, the study will elucidate the role of these chemicals in the gut-brain axis and the ND disease development after digestion. The neuroprotective and neurodisrupting compounds from organic, conventional, and processed tomatoes will be characterised by mass spectrometry. In vitro colon models will be employed to study the fate of these compounds in the gut and identify gut-microbial metabolites and their effect on intestinal epithelium cells.
(Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions MSCA) The current global biodiversity crisis requires rapid, inexpensive and reliable methods of detecting the main threats to species’ survival: pathogens, habitat change, and loss of genetic diversity1. Equally crucial are solutions for stemming biodiversity loss: we lack vital models that determine how these threats interact, which would help prioritise conservation efforts. Recently, CRI-CG has discovered for one species of frog over a relatively small geographic area that eDNA extracted from water samples captures more genetic diversity than analyses using tissue samples (UNESCO-funded project ACQUAVIVA). The same eDNA can be used to detect amphibian pathogens. NIPMAP will apply this knowledge in an innovative way by: i) optimizing this eDNA approach to estimate mtDNA diversity in four amphibian taxa (two caudates, two anurans) and pathogen diversity (principal pathogens: Bd, Bsal, Rv) across the eastern Italian Alps; ii) using these data to inform individual-based and spatially explicit simulations of host movements and pathogen transmission37; iii) integrating parameters from i-ii with skin microbiota and other health indices, as well as iv) environmental variables at each sample site, to generate correlative models (e.g. GLMMs and SDMs) and potential distribution maps to direct conservation management decisions. We will also pilot two innovative eDNA protocols: one to measure nuclear DNA diversity (to measure current gene flow and dispersal rates) and one to understand microbiota function using metatranscriptomics. These interdisciplinary tools will be integrated into a workflow that will be applicable to animal taxa anywhere on the planet.
Promuovere la sostenibilità e l'innovazione agricola attraverso la coltivazione di noce, castagno e piante medicinali e aromatiche.
(Fondazione CARIVERONA) Il progetto ha come principale obiettivo quello di definire le migliori modalità di impollinazione incrociata dell'olivo nell’areale gardesano e quindi limitare alternanza di produzione attraverso un approccio bottom-up:
- Validare, su base genetica, la composizione varietale olivicola presente nel territorio gardesano e determinare fonti di variazione genetica (i.e. cultivar non Casaliva/Grignan) da sfruttare per test impollinazione incrociata
- Determinare il grado di auto-incompatibilità (effetto negativo su allegagione/produttività) delle cultivar Casaliva e Grignan in relazione a condizioni climatiche contrastanti e note per indurre meccanismi preferenziali rivolti alla auto-incompatibilità o all’impollinazione incrociata in olivo
- Definire un gruppo di cultivar, sia selezionate da obiettivo 1) che varietà impollinatrici non autoctone, che mostrano polline ad alta compatibilità con le varietà di interesse produttivo (aumento allegagione/produttività in Casaliva e Grignan)
- Validare le cultivar impollinatrici attraverso la comparazione di sincronia fenologica e la definizione di un piano di fioritura che permetta la completa sovrapposizione tra impollinatori, Casaliva e Grignan.
- Individuare, sia in ambiente semi-controllato che in campo, la sensibilità delle cultivar selezionate a condizioni climatiche avverse (alte-basse temperature, alta-bassa umidità relativa, ridotta disponibilità idrica) basandosi su caratterizzazione fisiologica fogliare, risposta fiorale (componenti di resa, numero fiori perfetti/imperfetti) e percentuale di riduzione di quantità e vitalità pollinica in ambiente sub-ottimale.
Attività FEM:
3) Analisi della vitalità del polline di olivo e carica pollinica. In particolare, per questi studi, si utilizzerà una nuova tecnica high-throughput che permetterà di processare un numero maggiore di campioni pollinici (Ampha Z32)
(Fondazione VRT) Obiettivi generali del progetto:
- Integrazione in DigiAgriApp della possibilità di riconoscere la presenza di vettori del fitoplasma per la Flavescenza Dorata su trappole cromotropiche
- segnalazione all'utente della presenza/assenza del vettore sulla foto della trappola cromotropica
- Realizzazione mappa distribuzione della presenza assenza del vettore del fitoplasma per la Flavescenza Dorata sul territorio
Attività FEM:
- Integrazione del modello di riconoscimento dei vettori del fitoplasma della Flavescenza dorata già sviluppato all'interno del server di DigiAgriApp
- Scrittura capitolato per lo sviluppo dei componenti necessari all'App
- Verifica del lavoro della ditta esterna da cui verrà sviluppato il modulo che verrà integrato in DigiAgriApp

PNRR Missione 6, Componente 2, Investimento 2.1 - "Rafforzamento e potenziamento della ricerca biomedica del SSN.
- Bando Ministero della Salute M6.C2.I2.1 Secondo bando Ministero della Salute M6.C2.I2.2
(POC Bando PNRR) verifies through nutritional studies the effect of a glucosinolate preparation on damage from neurodegenerative diseases.
FEM activity: untargeted and targeted metabolomic analysis (tryptophan metabolites, SCFA) on blood and urine samples, and extraction of glucosinolates from plant matrices.
(PRIMA FOUNDATION) Mediterranean diet (MD) has long been considered a landmark in healthy nutrition, but changing eating habits has meant that people have become less adherent to it. The younger population lost the connection with traditional foods while older people experience life changes that result in significant swaps in their diet.
Despite this, both groups could benefit from a diet rich in antioxidants that has been shown to help prevent disease over the long term.
PROMEDLIFE aims to reverse, through a multi-actor approach, the decline in adherence to the MD pattern, adopting four lines of intervention.

PNRR - Mission 1 - Digitization, innovation, competitiveness and culture; Component 3 - Culture 4.0 (M1C3), Measure 2 "Regeneration of small cultural sites, cultural, religious and rural heritage"; Investment 2.3: "Programs to enhance the cultural identity of places: historical parks and gardens"
- Funding: € 552.662,15
- CUP: D19D22000020006
(EUREGIO) The melting of rock glaciers (permafrost) and glaciers is often a source of enrichment in trace metals for high-altitude waters, where they reach concentrations that can exceed legislative limits for human use, thus affecting the chemical and biological quality, and functionality of Alpine aquatic ecosystems.
This project aims to understand and quantify the origin, fate, and effects of these trace elements in three glacial and periglacial basins on the north and south slopes of the central and eastern Alps, with a focus on abiotic and biotic processes that alter the concentration of metals in water and trophic networks (assimilation, bioaccumulation).
Cultivating Rhodiola rosea in aeroponics, optimizing growth, extracting anti-inflammatory compounds, and evaluating their bioactivity
(EUREGIO) Come dichiarato negli obiettivi del millennio delle Nazioni Unite, una delle maggiori sfide per l'umanità è la riduzione della fame entro il 2030 e la garanzia di cibo per gli attesi 8,3 miliardi di persone nel mondo. Di conseguenza, si prevede un significativo aumento dell'uso di pesticidi sintetici al fine di ottimizzare la resa delle colture. Tali pesticidi comportano, tuttavia, gravi effetti negativi sulla salute ambientale e umana.
La frutta e in particolare l'uva sono tra le colture che richiederanno l'uso più abbondante di fungicidi soprattutto contro la peronospora causata dal patogeno oomicete Plasmopara viticola. Si stima che due terzi di tutti i fungicidi sintetici attualmente impiegati in agricoltura nell'Unione europea vengano utilizzati per controllare la peronospora della vite. Di conseguenza P. viticola è diventato recentemente resistente a molti fungicidi. Pertanto, la ricerca e lo sviluppo di strategie alternative per controllare le infezioni da P. viticola sono urgentemente necessari. In alternativa all'uso di sostanze chimiche tossiche, viene proposto un nuovo tipo di prodotto fitosanitario basato sull'azione di piccoli RNA (siRNA) interferenti rivolti specificamente a P. viticola.
(PSR PAT 2014-2022) The PEI (European Innovation Partnership) project "SMS Green - Circular Bioeconomy: apple-soil sustainability" (abbreviated as SMS Green) aims to close the circle of the fruit supply chain related to apple cultivation, production and processing, applying the principles of bioeconomy, through the introduction of technological and management processes that allow the recovery and valorization of by-products and waste materials for the production of energy from renewable sources and quality soil improvers to be returned to the soil for the restoration of fertility and maintenance of biodiversity.
(Horizon Europe MSCA Postdoctoral Fellowships 2022) The biodiversity hypothesis asserts there is a link between the diversity of environmental and host-associated microbes and ‘civilization diseases', such as asthma and allergies, the result of immune dysfunction and chronic inflammation. Using a well-studied rodent model, the bank vole, SOIL2GUT will test for the first time whether exposure to natural communities of soil microbes during development can improve individual health by promoting microbiota function at the host-microbiota interface (ileum and colon mucous layers) and reduce the risk of immune-related diseases. SOIL2GUT will take advantage of tissue samples generated by an ongoing intervention experiment, promoting the 3Rs policy, but also providing a unique opportunity for ‘omics integration (metataxonomics + MTX). Innovatively, this project will focus on the function of gut flora (not merely taxonomical characterization), in both bacteria and fungi (the latter is particularly unusual), using recent developments in metatranscriptonomics (MTX) to explore functional activity, and combining metadata and metatranscriptomes in statistical models to identify critical factors determining health. Since 68% of the human population will be urbanized by 2050, SOIL2GUT will contribute significantly to the WHO OneHealth framework. This project will also provide data that can be used to plan urban greenspaces, enhance rewilding interventions and improve domestic and zoo animal wellbeing. The researcher will build on his previous experiences and solid publications as a PhD/postdoc, receiving advanced personalized training in bioinformatics and soft skills, including writing grant applications for expanding to other tissues (lung, skin), and rendering him highly employable. In exchange, the researcher will bring methods for measuring individual health and immune gene expression to the hosting lab, among others. A synergy of expertise in microbiota research is envisaged, leading to future collaborative endeavors.
Keywords:
microbial ecology, ecosystem microbiota, metatranscriptomics, wild rodent model, conservation 'omics
(MOORE FOUNDATION) Global-scale assessment of behavioral responses of wildlife to COVID-19 lockdowns (in collaboration with the International Bio-Logging Society)
(Fondazione VRT) L’inquinamento acustico può avere effetti negativi sia sulla fauna sia sul benessere umano, che sono ad oggi per lo più ignoti, specialmente in contesti non urbani. Servono quindi strumenti ad hoc che permettano di distinguere tra suoni di 'buona qualità' e suoni di 'cattiva qualità', ovvero quelli che generano inquinamento acustico. Questo progetto prevede lo sviluppo e la sperimentazione di sensori per distinguere le sorgenti di inquinamento acustico da altri suoni che possono avere effetti anche benefici sull'uomo e sulla natura stessa. Lo sviluppo di questi sensori, che sono peraltro estremamente duttili, essendo applicabili in contesti ambientali diversi (urbano, periurbano, rurale) si pone quindi come elemento per tutelare sia il benessere dei cittadini, sia la tutela di specie (es. galliformi, Ungulati).
(Fondazione VRT) Obiettivi generali del progetto: Sviluppo di metodologie analitiche innovative per garantire la qualità e migliorare la rintracciabilità della filiera del tartufo
(PSR PAT 2014-2022) The aim of the project is to develop, in a circular economy perspective, a local supply chain for the recovery and valorization of food by-products to produce, through insect rearing, new sources of alternative proteins with a low environmental impact to be used in the feed sector for livestock (farm animals), in particular chickens and fish. Different by-product mixtures are studied on reared larvae in order to define the influence of diet on the larvae. The next part of experimentation, involves feeding fresh or processed (frozen or within a feed) larvae to chickens and fish and testing their zootechnical performance.
FEM activities:
Experiments on different diets in fish, particularly for DNA extraction from fecal sample and subsequent molecular amplification of the region of interest for analysis with Illumina MiSeq technology. Meta-taxonimic analysis of the data obtained. RNA extraction from intestinal tissue for the study of gene expression of inflammation markers. The analyses aim to study the influence of diet on the one hand on the microbial ecology in the fish intestine and on the other hand on tissue inflammation levels.
(Fondazione VRT) Il progetto punta a creare mappe di facile consultazione, che mostrano il rischio di presenza e attività di zanzare e zecche nella provincia autonoma di Trento. Utilizzando modelli di intelligenza artificiale e machine learning, verranno analizzati dati climatici e ambientali per prevedere dove e quando questi artropodi sono più attivi. Queste mappe, fruibili online, aiuteranno la popolazione a proteggersi dalle punture di zanzare e zecche, migliorando la salute pubblica e la qualità della vita.
Attività FEM: Analisi dati e elaborazione modelli statistici.
